Web Programming
Lecture 2
CSS
Seoul National University of Science and Technology
Information Technology Management
Lecture slides index
March 10, 2025
Agenda
What are we going to learn?

Analogy of a web page

Words + images
HTML

CSS
JavaScript
Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes the appearance and layout of information on a web page (as opposed to HTML, which describes the content structure)
- Can be embedded in HTML (bad) or placed into separate .css file (much better)
Best Practice
To keep your code clean and easier to mantain, separate your styling into its own file.
Basic CSS Rule Syntax
- A CSS file consists of one or more rulesets containing one or more rules
- Selectors designate exactly which element(s) to apply styles to
- Properties determine the styles that will be applied to the selected element(s)
- Each property has a set of values that can be chosen
- There are currently over 200 possible style properties to choose from - VSCode is useful for autocompleting property values!
- A rule is considered a selector and the list of properties applied to it.
style attribute and tag embedded in HTML
- In general, it is better to put your styles in external stylesheets and apply them using
<link>elements.
Common CSS properties
| CSS Property | Example Values |
|---|---|
color |
red, blue, #000000 (black) |
text-align |
left, right, center, justify |
width, height |
auto, 100px, 50%, 100% |
margin, padding |
0, 10px, 20px, 1em |
font-family |
Arial, Times New Roman, sans-serif, serif |
font-size |
12px, 16px, 1.5em, |
font-weight |
normal, bold, 400, 700 |
border |
none, 1px solid black, 2px dashed red, 3px double blue |
Grouping selectors
Allows us to reduce redundancy by grouping together rules into rulesets to style multiples types of elements with common styles. What will text inside the <p> tag look like here?
id and class
id
- Unique identifier for an element
- Each unique id can only appear once per page
- Each element can only have one id
class
- Non-unique grouping attribute to share with many elements
- Many elements (even of different types) can share the same class
- Each element can have many different classes
Cascade and specificity
All styles “cascade” from the top of the sheet to the bottom
Source Order: If multiple CSS rules have the same specificity, the one that appears later in the stylesheet overrides earlier ones.
Specificity: More specific selectors (like IDs) override less specific ones (classes, tags).
- inline
- id
- class
- type
Importance (!important): Styles marked with !important override specificity and source order, becoming top priority.
The Document Object Model (DOM)
How the browser represents the hierarchy of a page. Very useful when thinking about selectors!
For example:
- Every HTML tag (
<p>,<em>,<body>, etc.) is part of the DOM, and has a place in a tree hierarchy. - They all have a parent (
<body>’s is<html>) and almost always have a child (<title>is a child of<head>). - You don’t build a DOM, but the browser does, which allows you to access it.
Example DOM
CSS Selectors
| Syntx | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
a, b |
Multiple Element Selector | |
a b |
Descendant Selector | Selects all b elements located anywhere inside of a |
a > b |
Child Selector | Selects all b descendants directly inside a elements |
a + b |
Adjacent Sibling Selector | Selects b only if it shares a parent with a and is immediately after it in the DOM |
[a=b] |
Attribute Selector | |
a:b |
Pseudoclass Selector | |
a::b |
Pseudoelement Selector |
Responsive web design
Adjusts a website’s layout to fit the screen size of the device it’s being viewed on.
It allows a single website to work across many devices, including desktops, tablets, and phones.
Responsive design related concepts:
- Viewport
- Media queries
- Layout techniques in CSS
Viewport
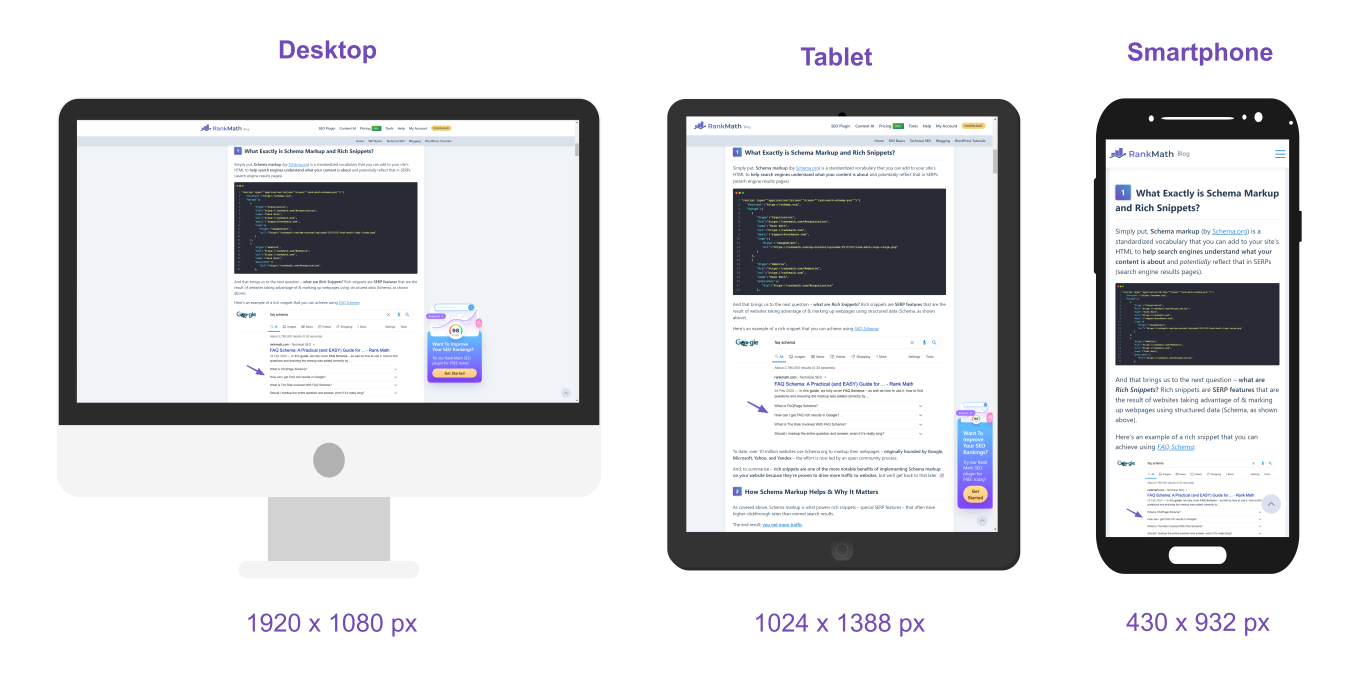
The viewport is the user’s visible area of a web page.
The viewport varies with the device, and will be smaller on a mobile phone than on a computer screen.
Media queries
Include this line in the <head> tag of your HTML document.
<meta name=viewport>tag is essential for controlling how a webpage fits into different screen sizeswidth=device-widthmatch the width of the viewport to the width of the deviceinitial-scale=1.0defines the zoom of the page the moment it loadsMedia types:
print,screen,hover, etc.
Media features:
height,width,orientation, etc.
Layout techniques in CSS
- Box Model (margin/padding/border)
- Flex
- Grid
- Others (we are not going to study them)
- Positioning
- Float (less common today)
CSS box model
The CSS box model module defines the margin and padding properties, which along with the height, width and border properties, make up the CSS box model.

Flexbox
- Flexbox is a set of CSS properties for aligning block level content.
- Flexbox defines two types of content: “containers” and “items”.
- “Container” (sometimes referred to as the flex parent): the direct parent element of the HTML elements whose position you would like to control
- “Items” (sometimes referred to as the flex children): the directly nested elements inside the parent container whose position you are controlling.
- Most properties on the container can be set to determine how its items are laid out. Some properties can be directly applied to the flex items.
To label the container as a flex container we use the CSS set
Flexbox
The aftermath of dipslay:flex

Basic properties of a flex container
display: flex;
-makes an element a “flex container”, items inside automatically become “items” - by default, starts as a row
justify-content: flex-end; (flex-start, space-around,…)
- indicates how to space the items inside the container along the main axis
align-items: flex-end; (flex-start, center, baseline,…) - indicates how to space the items inside the container along the cross axis
flex-direction: row; (column) - indicates whether the container flows horizontally or vertically (default row)
flex-wrap: wrap; (no-wrap, …) - indicates whether the container’s children should wrap on new lines
The Impact of Adjusting flex-direction
- The default
flex-directionis row. If you change theflex-directionto column you are changing the orientation of the axes. - The properties arranging elements along each axis does not change
- Example:
justify-contentstill controls items along the main axis. The main axis is just vertical now
![]()
- Example:
CSS grid layout
It divides the page into major regions and defines the relationship in terms of size, position, and layering between parts of a control built from HTML primitives.
To label the container as a grid container we use the CSS set
grid-column-gapandgrid-row-gapspecifies the gap between the columns and rowsgrid-template-columnsandgrid-template-rowsspecifies the size of the rows in a grid layout
Bootstrap
Bootstrap is one of the most popular HTML, CSS, and JavaScript framework for developing responsive, mobile-first websites.
Bootstrap is opensource under the MIT license .
- Include this code in your
<head>element of your HTML document
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-QWTKZyjpPEjISv5WaRU9OFeRpok6YctnYmDr5pNlyT2bRjXh0JMhjY6hW+ALEwIH" crossorigin="anonymous">
Next week
Say hello to our new friend, JavaScript…

Acknowledgements
- Some contents of this lecture are partially adapted from:
- Harvard CS50’s Web Programming with Python and JavaScript, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Materials from University of Washington’s CSE 154 Web Programming (used with permission).
- The Odin Project (main website code under MIT license and curriculum licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
- The Fundamentals of Web Application Development (Web Edition) ©2025 Nicholas D. Freeman. All rights reserved. The content is provided for educational purposes only and is not an exhaustive treatment of the subjects.

Web Programming


