Web Programming
Lecture 10
More on Node, POST and Full Stack Websites
Seoul National University of Science and Technology
Information Technology Management
Lecture slides index
May 13, 2025
Agenda
- Node.js middleware pattern
- POST and forms
- Full Stack Node.js simple app
- File I/O
Course structure

Starting a Node.js Project
- There are a few steps to starting a Node.js application, but luckily most projects will follow the same structure.
- When using Node.js, you will mostly be using the command line
- Start a new project directory (e.g. intro-node)
- Create your
app.jsfile in your project directory - Inside the directory, run
npm initto initialize apackage.jsonconfiguration file (you can keep pressing Enter to use defaults) - Install any modules with
npm install <package-name> - Write your Node.js file! (e.g.
app.js) - Include any front-end files in a public directory within the project.
- Along the way, a tool called npm will help install and manage packages that are useful in your Node app.
Starting app.js
- Run
npm install expressto install the Express.js package - Build your baisc app with the following file
- Check if your service is running correctly accessing this in your browser http://localhost:8080/posts
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 8080;
app.get('/posts', function (req, res) {
console.log("Endpoint /posts received a GET request.");
res.type("text").send("Hello World");
});
app.listen(8080, () => {
console.log(`Our first node app listening on port ${PORT}`);
});POST Parameters
- Since POST parameters are sent through the body of the request, there is no guarantee that they are set, therefore, they must be checked before using them/assuming they exist
Handling Different POST Requests
- POST requests can be sent with different data types:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/json
- multipart/form-data
- In Express, we use the middleware pattern to extract the POST parameters from the
req.body. - For the first two types, there is built-in middleware - we don’t need middleware for text/plain.
- With forms and fetch, we use the
FormDataobject to send POST parameters, which is always sent as multipart/form-data. - There is no built-in middleware to access the
req.bodyparams for multipart content.
Middleware & Request/Response Pipeline
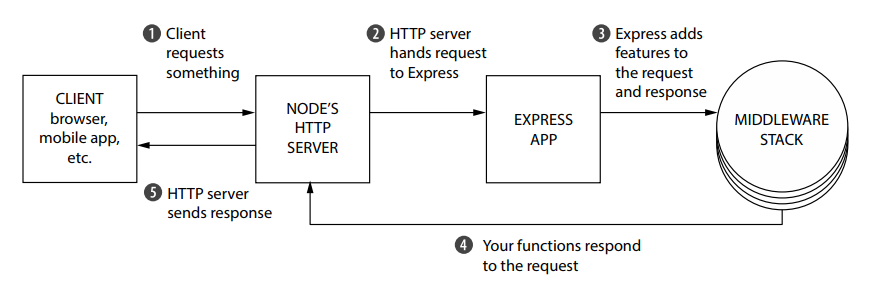
- The heart of Express is the middleware pattern, which allows you to extend the functionality of the framework by adding functions that will be executed in the request-response cycle.
- The middleware functions are executed in the order that they are added to the application,
- The middleware pattern as a pipeline, where the request is passed through the pipeline, and each middleware function can modify the request and the response, and pass the request to the next middleware function in the pipeline.
Full Stack Project Directory
- When creating full stack projects (both frontend and backend), your project directory should include all the static forward facing files in a folder named public and everything else at the root.
Connecting a frontend to a backend
- These three lines of code allow your code to run on a specified port and look into a specific directory for files to serve to the user.
- They must be included at the bottom of your app.js file.
Connecting a frontend to a backend
Client side
- This requires you have your directory structure and
app.jsfile configured properly AND that you are accessing your HTML document through localhost
Supporting incoming GET and POST requests
- GET requests
- Information sent through URL
- Retrieving non sensitive information
// GET endpoint
app.get('/path/:key', (rq, rs) => {
let ex1 = rq.params.key
let ex2 = rq.query.key
}- POST requests
- Informations sent through the body
- Sensitive information and/or updating state
Full Stack Books app
Simple book registry (title & author)
RESTful API endpoints (GET / POST)
Data stored in-memory
Static HTML pages consuming API via fetch()

In-memory API setup
- Initialize project: npm init -y
- Install deps: express, body-parser, cors
- body-parser
- bodyParser.json() → parses JSON request bodies into req.body
- bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }) → parses HTML form data
- cors
- Enables Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
- Allows browser
fetch()from different origins - Usage:
app.use(cors());
- body-parser
- Create app.js and require modules
- Define const books = []
Define Endpoints
GET /api/books→res.json(books)POST /api/books→ validate body →books.push(...)→res.status(201).json(...)- Start server:
app.listen(PORT)
// endpoint for getting a list of books
app.get('/api/books', (req, res) => {
res.json(books); originally
});
// endpoint for adding a book
app.post('/api/books', (req, res) => {
const { title, author } = req.body;
if (!title || !author) {
console.log("Error 400. Title and author required");
return res.status(400).json({ error: 'Title and author required' });
}
const newBook = { id: books.length + 1, title, author };
books.push(newBook); == this goes first
console.log("Code 201. Book created successful");
res.status(201).json(newBook); // HTTP 201 Created successful response status code
});Testing the API via Browser
//add.html
document.getElementById('addBook').onsubmit = e => {
e.preventDefault();
const form = e.target;
const payload = {
title: form.title.value,
author: form.author.value
};
fetch('/api/books', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
}).then(() => location.href = 'index.html');
};- Create a
public/folder in the root of the project - Serve it:
app.use(express.static('public')); - index.html
<script>uses fetch(‘/api/books’) to list books - add.html
<form>+ JS fetch() POSTs to /api/books
- Open http://localhost:8080/index.html to verify
- Create
public/styles.css
File I/O in Node.js
- Unlike the browser, we have access to the file system when running Node.js
- We can read all kinds of files, as well as write new files
- For this, we use the
fscore module - We saw express as our first module in Node.js to create an API
- And body-parser to parser POST request bodies
- Another useful module: fs (file system)
- This is a “Core” Module, meaning we don’t have to npm install anything.
- There are many functions in the fs module (with excellent documentation)
- Most functions rely on error-first callbacks, but we’re going to use the Promise versions
Reading Files and Writing Files
fs.readFile(fileName, encodingType)- fileName: (string) file name
- encodingType: file encoding (usually “utf8”)
- Returns: Promise with a value holding the file’s contents
fs.writeFile(fileName, contents)- fileName: (string) file name
- contents: (string) contents to write to file
- Returns: Promise without any resolved arguments
Reading Files and Writing Files with callbacks
- To read and write files, we first need the FileSystem package
const fs = require('fs');
Write file
fs.writeFile('hola.txt', 'Hola mundo', (err) => {
if (err) {
console.log(`Error: ${err}`);
} else {
console.log('File successfully written!');
}
});Read file
Reading Files and Writing Files with Promises
- We can ‘promisify’ the readFile function so that it returns a promise instead of taking a callback.
- We use the promises functions of fs
fs.promises
Using .then/.catch
let contents = fs.promises.readFile('hola.txt', 'utf8');
contents
.then(console.log)
.then(() => { console.log('Done reading file!'); })
.catch(err => console.log(`Error: ${err}`));Using async/await
Parsing JSON file contents
- You can read any file, including JSON.
- To parse JSON file contents and use as a JS object, use
JSON.parse
Writing and Reading JSON
- JSON files are text representations of JS objects. When you read from them, you will get a big string.
- When you write to them, you need to write a string.
JSON.parse(jsonString)to turn a JSON string into an objectJSON.stringify(jsonObj)to turn a JSON object into a string
// Read JSON file and return parsed object
async function readJSON(filePath) {
const data = await fs.promises.readFile(filePath, 'utf8');
return JSON.parse(data);
}
// Write object to JSON file
async function writeJSON(filePath, jsonObject) {
const data = JSON.stringify(jsonObject);
await fs.promises.writeFile(filePath, data);
}Next week
- Data Persistence in Node.js
Acknowledgements
- Some contents of this lecture are partially adapted from:
- Harvard CS50’s Web Programming with Python and JavaScript, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Materials from University of Washington’s CSE 154 Web Programming (used with permission).
- The Odin Project (main website code under MIT license and curriculum licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
- The Fundamentals of Web Application Development (Web Edition) ©2025 Nicholas D. Freeman. All rights reserved. The content is provided for educational purposes only and is not an exhaustive treatment of the subjects.
- freeCodeCamp.org © 2025 freeCodeCamp.org. All rights reserved. The content is provided for educational purposes only and is not an exhaustive treatment of the subjects.
- Node.js for Beginners by Ulises Gascón. Some contents adapted under fair educational use for instructional purposes.

Web Programming