Web Programming
Lecture 1
HTML
Seoul National University of Science and Technology
Information Technology Management
Lecture slides index
March 10, 2025
Agenda
What are we going to learn?

Analogy of a web page

Words + images
HTML

CSS
JavaScript
HTML
Hyper: over/above/beyond
Text: words and/or alphanumeric characters
Markup: the result of preparing text or indicating the relationship between parts of text before displaying
Language: a system of symbols used to communicate ideas
In other words… HTML defines the meaning and structure of web content(i.e., text, images, etc.)
Hypertext Markup Language
- Describes the content and structure of information on a web page
- Not the same as the presentation (appearance on screen)
- Surrounds text content with opening and closing tags
- Most whitespace is insignificant in HTML (ignored or collapsed to a single space)
- We will use a newer version called HTML5
Structure of an HTML page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Web Programming ITM</title>
</head>
<body>
Welcome to Spring Semester!
</body>
</html>Main HTML tags
<!DOCTYPE html>tells the browser to interpret our page’s code as HTML5<html>Represents the root (top-level element) of an HTML document<head>Contains machine-readable information (metadata) about the document (not rendered)<body>contains the page’s content
General Outline with HTML5 <body>
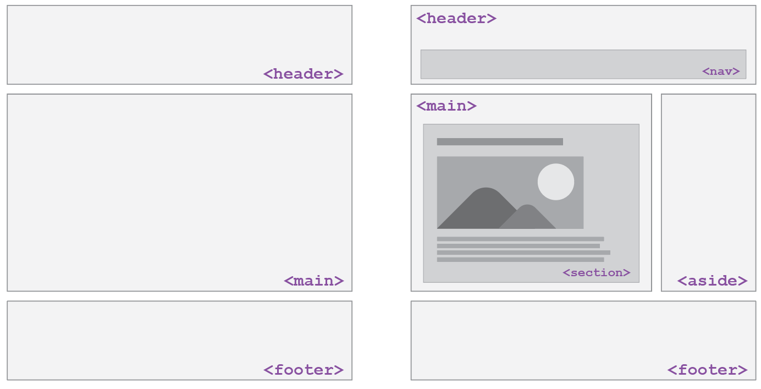
HTML5 Semantic Tags
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer
<main>- Main content of the document
- there can only be one main element in the
<body> - The content inside should be unique and not contain content that is repeated across pages ( e.g. sidebars, nav link, search bars, etc.)
<header>- contains header information for page body or section/article, including logos, navigation bar, etc.
<footer>- contains footer information for page body or section/article, including copyright information, contact, links, etc.
HTML5 example semantic structure
Common HTML tags
HTML heading levels <h1>…<h6>
- Represent heading information for portions and/or subportions of the page
<h1>: highest importance,<h2>: second highest importance etc.- Do not choose based off of the rendered size
- Remember, what is the purpose of HTML? -Do not skip heading levels
Do not confuse this tags
<head> vs. <header> vs. <h1>…<h6>
Ordered <ol> and unordered <ul> lists
<ul>for an unordered list (typically a bulleted list)<ol>for an ordered list (typically a numbered list)- Both represent a list of items
<li>tags are used within both unordered AND ordered lists<li>list item tag. Representative of an item in a list- A list can contain another list
Images <img>
Inserts a graphical image onto the page (inline)
- The
srcattribute specifies the image URL - The
altattribute describing the image, which improves accessibility for users who can’t otherwise see it.
Example


Link (Anchors) <a>
Links, or “anchors”, to other pages (inline)1
Uses the href (Hypertext REFerence) attribute to specify the destination URL Can be absolute (to another web site) or relative (to another page on this site)
- Absolute example: “https://www.google.com/”
- Relative example: “/img/figure.jpg”
Example
Output
Search for it on Google!
Relative vs absolute paths for links and images
Relative: paths are relative to the document linking to the path. - Linked files within the same directory: “filename.png”
- Linked files within a subdirectory (e.g. “img”): “img/filename.jpg”
Absolute: paths refer to a specific location of a file, including the domain and protocol.
- Typically used when pointing to a link that is published online (not within your own website).
- Example:
"https://validator.w3.org/"
Tables <table>
Allows web developers to arrange data into rows and columns.
<td>defines a table cell (table data)<tr>defines a table row<th>defines a table header (optional)<thead>groups the header content in a table<tbody>groups the body content in a table
Forms <form>
It is used to create an HTML form for user input.
<input type="text">displays a single-line text input field<input type="submit">Displays a submit button (for submitting the form)<input type="button">Displays a clickable button
Next week
Give style to our HTML document with CSS
Acknowledgements
- Some contents of this lecture are partially adapted from:
- Harvard CS50’s Web Programming with Python and JavaScript, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Materials from University of Washington’s CSE 154 Web Programming (used with permission).
- The Odin Project (main website code under MIT license and curriculum licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
- The Fundamentals of Web Application Development (Web Edition) ©2025 Nicholas D. Freeman. All rights reserved. The content is provided for educational purposes only and is not an exhaustive treatment of the subjects.

Web Programming