Computer Language
Lecture 3
Part 1 : Variables
Seoul National University of Science and Technology
Information Technology Management
Lecture slides index
April 14, 2025
Class contents
- Introduction to Computer Programming and Java
- Reading Input and Strings
- Variables and calculation with numbers
- Conditional statements
- Repeating functionality
- Methods & Debugging
- Lists, Arrays and Strings
- Midterm
- Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
- Deeper look into Object Oriented Programming
- Inheritance and Interfaces I
- Inheritance and Interfaces II
- Class diagrams, packages and exceptions
- Project Live Code Review and Evaluation
- Final examination
Class contents
- Introduction to Computer Programming and Java
- Reading Input
- Variables and calculation with numbers
- Conditional statements
- Repeating functionality
- Methods & Debugging
- Lists, Arrays and Strings
- Midterm
- Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
- Deeper look into Object Oriented Programming
- Inheritance and Interfaces I
- Inheritance and Interfaces II
- Class diagrams, packages and exceptions
- Project Live Code Review and Evaluation
- Final examination
Agenda
- Introduction to variables
- Variable assignment
- Tracing code with variables
- Naming conventions
- Reading different type of variables
Objectives
- Understand the concept of a variable.
- You know what variable types, names, and values are.
- Know how to create and use string, integer, floating-point, and boolean variables.
Introduction to variables
We’ve already familiarized ourselves with strings to a degree while dealing with user inputs.
Let’s turn our attention to learning about other variable types commonly used in Java.
A variable can be thought of as a container in which information of a given type can be stored.
Examples of these different types include text (
String), whole numbers (int), floating-point numbers (double), and whether something is true or false (boolean).
Variable assignment
A value is assigned to a variable using the equals sign (=).
In the statement above, the value of 12 is assigned to an integer variable called months. The statement could be read as: “the variable months is assigned the value 12”.
Joining variables and strings
A variable’s value can be joined to a string using the + sign, as seen in the following example:
String text = "contains text";
int wholeNumber = 123;
double floatingPoint = 3.141592653;
boolean trueOrFalse = true;
System.out.println("Text variable: " + text);
System.out.println("Integer variable: " + wholeNumber);
System.out.println("Floating-point variable: " + floatingPoint);
System.out.println("Boolean: " + trueOrFalse);Exercise 1 - Various variables
The Code template tab contains a program that prints the output shown in the Sample Output tab.
Modify the program in the right places so that it prints the output shown in the Modified output tab.
public class VariousVariables {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MODIFY THESE:
int numberOfChicken = 3;
double baconWeight = 5.5;
String tractor = "None!";
// DON'T MODIFY THESE:
System.out.println("Chicken:");
System.out.println(numberOfChicken);
System.out.println("Bacon (kg):");
System.out.println(baconWeight);
System.out.println("Tractor:");
System.out.println(tractor);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("And finally, a summary:");
System.out.println(numberOfChicken);
System.out.println(baconWeight);
System.out.println(tractor);
}
}Variable names
- Variable names are unique - no two variables can have the same name.
- The program in the following example is faulty as it attempts to create the variable
pitwice. - The variable is created the first time its declared.
Variable type
- The variable type is stated when the variable is first declared (Line 1).
- When a new value is assigned to the variable, the type is no longer declared (Line 3).
Sample output
Changing a value assigned to a variable
- A variable exists from the moment of its declaration, and its initial value is preserved until another value is assigned to it.
- You can change a variable’s value using a statement that comprises the variable name, an equals sign, and the new value to be assigned.
int number = 123;
System.out.println("The value of the variable is " + number);
number = 42;
System.out.println("The value of the variable is " + number);Output
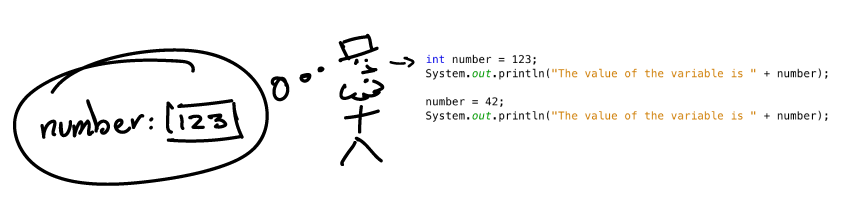
Tracing the code with variables (I)
Let’s look at the preceding program’s execution step-by-step.
- When a variable appears in the program for the first time, i.e., the computer is told both its type (in this case
int) and its name (in this casenumber), the computer creates a ‘named container’ for the variable. - Then, the value on the right side of the equals sign is copied into this named container.
Tracing the code with variables (II)
- Whenever a variable is referenced by its name in a program – here, we want to print the string “The value of the variable is” followed by the value of the
numbervariable – its value is retrieved from a container that has the corresponding name.

Tracing the code with variables (III)
- Whenever a value is assigned to a variable (here
number = 42), a check is run to see whether a container with the given name already exists. - If one does, a new value is copied in the place of the old value, and the old value disappears.
- If a container of the variable name is not found, the program execution ends in an error message, or it fails to run.

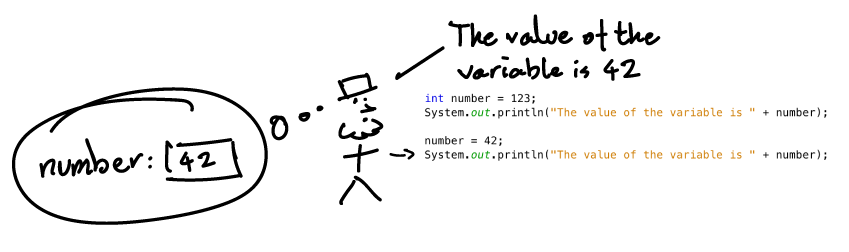
Tracing the code with variables (IV)
- The variable is then referenced again by its name in the program – we again want to print the string “The value of the variable is” followed by the value of the
numbervariable. - We proceed as normal, retrieving the value of
numberfrom a container having its name.
Tracing the code with variables (V)
- At the end of the program, you’ll notice that the original value of the variable has vanished.
- A variable can hold only one value at a time.
Variable’s type persists
- Once a variable’s type has been declared, it cannot be changed.
- For example, a boolean value cannot be assigned to a variable of the integer type, nor can an integer be assigned to a variable of the boolean type.
boolean integerAssignmentWillWork = false;
integerAssignmentWillWork = 42; // Does not work
int value = 10;
integerAssignmentWillWork = value; // Neither does this- However, an integer can be assigned to a variable of type double, since Java automatically converts the integer to a double.
Naming Variables
- Naming variables is a fundamental aspect of describing a program. Let’s look at two examples.
- Both of the preceding examples function the same way and output the same result.
- One of them is, however, much more understandable.
- The objective here is to compute the surface area of a circle.
- The value of pi is defined in the first row, the circle’s radius in the second, and the surface area calculated in the third.
Note on variables names
Variables Express the Program and the Problem to Be Solved
Programming is a problem-solving tool.
The aim is to create solutions for any given problem, such as the automation of control in cars.
As a problem is approached, the developer decides on the terms used to describe the problem domain.
The terminology that is chosen, such as variable names, will serve to describe the problem for anyone who is to work with it in the future.
As you’re wording the problem that you’re solving, think about the concepts related to that problem and appropriate terms that could be used to describe them.
If you find it hard to come up with relevant names, think of the ones that definitely do not describe it.
After this, settle on some terminology that you’re going to use – the good thing is that you can usually improve on it later on.
Variable naming conventions (I)
Variable naming is limited by certain constraints.
- Variable names cannot contain certain special symbols, such as exclamation marks (!).
- Spaces are also not allowed, since they’re used to separate parts of commands. Instead of spaces, the convention in Java is to use a style known as camelCase.
Variable naming conventions (II)
- Numbers can be used within a variable name as long as the name does not begin with a number. Also, a name cannot consists of numbers only.
int 7variable = 4; // Not allowed!
int variable7 = 4; // Allowed, but is not a descriptive variable name- A variable’s name cannot already be in use.
- These names include, for instance, variables previously defined in the program and commands provided by Java, such as
System.out.printandSystem.out.println.
Variable naming conventions (III)
- Letters containing diacritics (e.g. the letters ä and ö used in Finnish) should also not be used in variable names.
- You can replace these letters with their non-diacritic equivalents. For example, you should convert ä -> a and ö -> o.
Permissible Variable Names
lastDayOfMonth = 20firstYear = 1952name = "Essi"
Impermissible Variable Names
last day of month = 201day = 1952beware! = 1910*1920 = 1
The type of the variable informs of possible values
A variable’s type is specified when it’s initally declared.
- For example, a variable containing the string “text” is declared with the statement
String string = "text";, and an integer having the value 42 is declared with the statementint value = 42;.
- For example, a variable containing the string “text” is declared with the statement
A variable’s type determines the types of values that can be assigned to it.
Stringtypes hold text,inttypes whole numbers,doublefloating-point numbers, andbooleantypes are either true or false.As such, the possible values of a given variable type are limited. For example, a string cannot contain an integer, nor can a double contain a boolean value.
Variable’s types
| Type | Example | Accepted values |
|---|---|---|
Whole number, i.e., int |
int value = 4; |
An integer can contain whole numbers whose values lie between -2147483648 and 2147483647. |
Floating-point number, i.e., double |
double value = 4.2; |
Floating-point numbers contain decimal numbers, with the greatest possible value being approximately 21023. When a decimal number is represented with a floating-point number, the value can be inaccurate as floating-points are incapable of representing all decimal numbers. |
String |
String text = "Hi!"; |
A string can contain text. Strings are enclosed in quotation marks. |
True or false value, i.e., boolean |
boolean right = true; |
A boolean contains either the value true or false. |
Reading from user
- In the text-based user interfaces that we’ve used in our programs, the user’s input is always read as a string, since the user writes their input as text.
- Reading strings from the user has become familiar by this point - we do it using the
nextLine-command of theScannerhelper method.
- Other input types, such as integers, doubles, and booleans are also read as text.
- However, they need to be converted to the target variable’s type with the help of some tools provided by Java.
Convert String to integer
- The
Integer.valueOfcommand converts a string to an integer. It takes the string containing the value to be converted as a parameter.
Output
Reading integers
- When using a
Scannerobject, the reading of the value is usually inserted directly into the type conversion. This happens like so:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Write a value ");
int value = Integer.valueOf(scanner.nextLine());
System.out.println("You wrote " + value);
}
}Output
Exercise 2 - Integer Input
Write a program that asks the user for a value and then prints the value provided by the user.
- Test the functionality of your program with non-numerical inputs.
- The program should break as it doesn’t know how to convert these inputs into numbers.
- We’ll learn how to deal with exceptional cases like these in the advanced programming course.
Convert String to double
- The
Double.valueOfcommand converts a string to a double. It takes the string containing the value to be converted as a parameter.
String valueAsString = "42.42";
double value = Double.valueOf(valueAsString);
System.out.println(value);Output
Reading doubles
- As with integers, the reading is nested within the conversion. This shown in the code below.
- It’s possible to also read an integer variable into a double, in which case the value is converted automatically to type double.
- Below there are two sample outputs, one for when the user inputs an floating-point number and one for when the user inputs an integer
Exercise 3 - Double Input
Write a program that asks the user for a floating-point number using the variable type Double. The program then prints the user’s input value.
Convert String to boolean
- The
Integer.valueOfcommand converts a string to an integer and theDouble.valueOfconverts it to a floating-point. - The
valueOfcommand also appears when converting a string to a boolean – this is done with the commandBoolean.valueOf. - Boolean variables can either have the value
trueorfalse. - When converting a string to a boolean, the string must be “true” if we want the boolean value to be
true. - The case is insensitive here: both “true” and “TRue” turn into the boolean value of
true. - All other strings turn into the boolean
false.
Convert String to boolean example code
Exercise 4 - Boolean Input
Write a program that asks the user for a boolean value. The program should then print the value provided by the user.
Example print 1
Example print 2
Summary
Finally, a summary:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String text = scanner.nextLine();
int integer = Integer.valueOf(scanner.nextLine());
double floatingPoint = Double.valueOf(scanner.nextLine());
boolean trueOrFalse = Boolean.valueOf(scanner.nextLine());
// and so on
}
}Exercise 5 - Different Types of Input
Write a program that asks the user for a string, an integer, a floating-point number, and a boolean. The program should then print the values given by the user.
Checking our learning objectives
- Understand the concept of a variable.
- You know what variable types, names, and values are.
- Know how to create and use string, integer, floating-point, and boolean variables.
Next
- Part 2: calculating with numbers
Acknowledgements
- Some contents of this lecture are partially adapted from:
- The Java Programming MOOC from the University of Helsinki, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.

Computer Language